Parkinson’s disease is one of the most common neurodegenerative diseases after Alzheimer’s.
It significantly impacts patients’ quality of life and their ability to perform daily activities.
With advancements in modern medicine, several surgical options have emerged, offering hope to patients whose traditional drug therapies are no longer effective in controlling their symptoms.
Neurosurgery for Parkinson’s disease is an advanced option aimed at alleviating extremely challenging symptoms.
It is only considered by specialized doctors and comes after medication fails to provide control.
Why Undergo Surgery for Parkinson’s Patients?
Parkinson’s disease is a progressive neurological disorder primarily affecting movement due to the damage of dopamine-producing cells in the brain.
While medications like levodopa are the cornerstone of early treatment, their effectiveness diminishes as the disease progresses.
This prompts doctors to recommend surgical intervention in specific cases. Modern surgeries, such as Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS), offer hope for patients with symptoms uncontrolled by medication.
However, surgery is not performed on all patients. It is reserved for intractable cases that no longer respond to medication or those experiencing severe complications from medications.
Accurate diagnosis and exclusion of other similar diseases are essential before deciding on surgery.
Main Types of Parkinson’s Surgeries
While Parkinson’s surgeries do not radically cure the disease, they are a powerful tool for managing symptoms in advanced stages.
Their success depends on careful patient selection, surgical expertise, and long-term follow-up.
Studies indicate that Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS) surgeries achieve high success rates in improving symptoms and reducing reliance on medication.
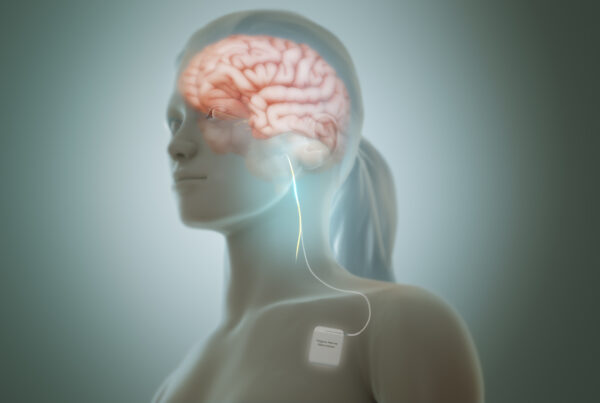
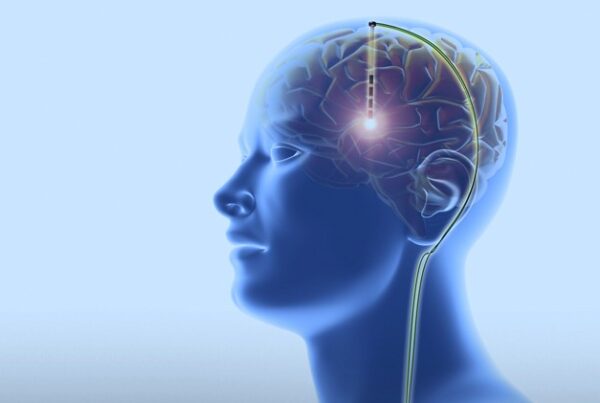
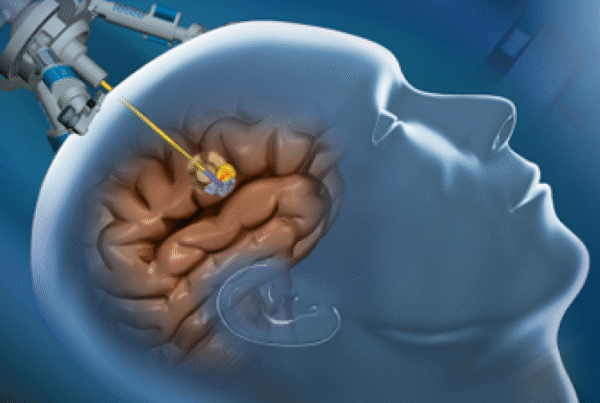
Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS)
Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS) is the most common and successful technique for treating Parkinson’s. It involves implanting electrodes in specific brain regions connected to a device under the skin.
Candidates for this procedure are individuals who experience bothersome “on-off” fluctuations despite medication, without severe dementia or psychiatric disorders. This technique reduces tremor and rigidity and generally improves movement.
Although the risk of complications is relatively low, it includes bleeding, infection, side effects in speech or balance, and some patients may experience confusion or mood changes.
Adaptive DBS, which automatically programs itself based on neural activity, represents a breakthrough. It received FDA approval in 2024, with reports of improved symptom levels and reduced medication usage.
- Success Rate: High improvement in motor symptoms for well-selected patients.
- Long-Term Results: Most patients report significant symptom improvement years after the operation.
- In Turkey: Liva Hospital is one of the leading centers for performing these operations, with excellent clinical outcomes for Arab patients.
Focused Ultrasound Surgery (FUS)
This is a non-invasive technique that uses high-frequency sound waves to destroy symptom-causing tissues without a surgical incision. It is approved for treating severe tremor.
- Advantages: Effective treatment for tremor in patients not eligible for traditional surgery.
- Studies: Clinical trials have shown significant improvement in motor symptoms in patients.
Radiofrequency Ablation
A fine probe is inserted to deliver heat waves targeting the areas responsible for symptoms, thereby disrupting abnormal activity.
- Effectiveness: Effective in treating severe tremor on one side of the body, with immediate symptom improvement.
- Indications: Suitable for patients unresponsive to other treatments or not eligible for traditional surgery.
Thalamotomy and Pallidotomy
Studies indicate that these operations achieve long-term improvement in motor symptoms, with caution regarding neurological complications.
- Thalamotomy: Effective in treating one-sided tremor and used when other treatments are not effective.
- Pallidotomy: Effective in treating involuntary movements caused by medications and improves motor symptoms.
Stem Cell Transplantation (Experimental)
Stem cell transplantation is a future technique aimed at replacing dopamine-producing cells.
Initial clinical trial results are promising in terms of safety and symptom improvement, but it has not yet been approved as a routine treatment.
It is an emerging research technique aimed at regenerating dopamine cells that are damaged as the disease progresses.
In some advanced centers, it is handled within the framework of clinical studies, where stem or embryonic cells are injected to gradually restore neurological functions.
Indications for Parkinson’s Surgeries
Neurosurgical procedures, such as Deep Brain Stimulation or ablative procedures, aim to improve motor ability and increase daily “on” time.
These experiences contribute to reducing reliance on medications and lessening the severity of tremor and rigidity, leading to a tangible improvement in daily functions and work.
This involves reducing “off” periods and achieving more stable motor fluctuations compared to full dependence on medication.
In some cases, patients are unable to continue high doses of medication due to the emergence of side effects such as dyskinesia, hallucinations, or general intolerance.
Therefore, surgical indications include:
- Lack of response to drug therapy or the appearance of severe motor fluctuations.
- Side effects of medications, such as involuntary movements.
- Deterioration of quality of life and loss of independence.
- Confirmed and stable diagnosis after excluding similar diseases.

After Surgery
After surgery, the follow-up and programming phase begins, which is crucial for maximizing the device’s benefits.
The device does not work at full capacity immediately; instead, it requires several doctor visits to precisely program the stimulation settings.
The intensity, frequency, and pulse width are adjusted based on the patient’s symptom response and side effects.
This process can take weeks or even months and requires patience and cooperation from the patient. Continuous patient education on how to use the device and handle any potential problems is an essential part of this stage.
In the long term, patients require regular follow-up with a neurologist to adjust settings as needed and to replace the battery when it runs out (typically every 3-5 years for non-rechargeable batteries, or longer for rechargeable batteries).
Conclusion
Parkinson’s surgeries represent a paradigm shift in treating patients for whom drug therapies are no longer sufficient. Surgical options vary, and each has specific indications depending on the patient’s condition.
The choice between neurosurgical procedures for Parkinson’s disease requires a comprehensive, individualized assessment.
This includes symptom severity, medication response, the patient’s psychological and mental state, and financial capacity.
Deep Brain Stimulation is the first choice in most cases, while ablative surgeries remain an alternative or temporary option in some circumstances.
Liva Hospital in Turkey is a leading center in this field, offering integrated medical services and successful experiences for patients from across the Arab world.
It provides accurate diagnosis and comprehensive pre- and post-surgical care, with excellent clinical outcomes for Arab patients.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the overall success rate of Parkinson’s surgeries?
Success rates for Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS) surgeries reach over 80% in improving motor symptoms and reducing reliance on medications.
Are all Parkinson’s patients eligible for surgery?
No, surgery is reserved for cases that no longer respond to drug therapy or experience severe complications from medications, and the diagnosis must be confirmed and stable.
What are the potential risks of Parkinson’s surgeries?
Risks include infection, bleeding, problems with the implanted device (in the case of DBS), or temporary or permanent neurological complications, depending on the type of surgery.
How long does the recovery period take after surgery?
The period varies depending on the type of surgery, but typically the patient needs a few days in the hospital, with ongoing medical follow-up and physical rehabilitation.
Can Parkinson’s surgeries be performed in Turkey for Arab patients?
Yes, Liva Hospital in Turkey offers comprehensive services for Arab patients, including reception, examinations, operations, and post-surgical follow-up.
Is stem cell transplantation approved as a treatment for Parkinson’s disease?
Currently, stem cell transplantation is still in clinical trials and has not been approved as a routine treatment for the disease.