Your arteries are like the vital road network in your body, transporting oxygen-rich blood and nutrients from the heart to every cell and organ.
They are responsible for delivering the essentials of life to your limbs, brain, and internal organs.
However, when these arteries become damaged or blocked due to conditions like atherosclerosis, blood flow significantly decreases or stops, threatening organ health and exposing the patient to serious risks that may lead to limb loss, stroke, or heart attack.
Facing these challenges, open artery replacement surgery is a critically important medical intervention aimed at restoring normal blood flow and saving threatened tissues, giving patients a real chance to regain their quality of life.
Fortunately, Liva Hospital in Turkey is one of the leading centers that performs this surgery according to precise protocols and advanced techniques to handle most cases.
Arterial Diseases Requiring Replacement
Arterial diseases, especially atherosclerosis, are the primary reason doctors consider artery replacement.
Atherosclerosis is a condition where fatty plaques accumulate inside artery walls, leading to their narrowing, hardening, and loss of elasticity.
The risk of these diseases increases with age and the presence of factors such as smoking, diabetes, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and obesity.
Early examinations and diagnosis play a crucial role in determining the need for surgical intervention.
This narrowing reduces blood flow and can lead to complete blockage. Common conditions requiring artery replacement surgery include:
- Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD): Affects arteries supplying the legs and arms. It can cause pain when walking (intermittent claudication), non-healing ulcers, and in severe cases, gangrene that may require limb amputation.
- Carotid Artery Disease: Narrowing in the carotid arteries in the neck that supply the brain. If a piece of plaque breaks off, it can block a blood vessel in the brain and cause a stroke.
- Aneurysm: A weakening in the artery wall that leads to its bulging or dilation, such as an Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm (AAA). If this aneurysm ruptures, it poses a fatal risk.
- Renal Artery Stenosis: Narrowing of the arteries supplying the kidneys, which can cause difficult-to-control high blood pressure or lead to kidney failure.
Preparing for Open Surgery
Preparation for open artery replacement surgery is a crucial stage to ensure the best outcomes and reduce potential risks.
This stage begins with a comprehensive medical evaluation of the patient, including a thorough review of medical history, a detailed physical examination, and a series of advanced diagnostic tests.
In addition to tests, the patient is provided with detailed instructions on how to prepare, which may include stopping certain medications and fasting.
The medical team provides psychological support and answers all patient inquiries to reduce anxiety and prepare the patient for the operation.
Among the important tests are:
- Comprehensive Blood Tests: To evaluate kidney and liver function, blood sugar and cholesterol levels, and clotting factors.
- Electrocardiogram (ECG) and Echocardiogram: To assess heart health and function, as a healthy heart is essential for tolerating surgery.
- Vascular Imaging (Angiography): Such as magnetic resonance angiography (MRA), computed tomography angiography (CTA), or vascular catheterization. These examinations provide detailed images of the affected arteries and determine the location and severity of the blockage or aneurysm.
- Lung Function Tests: To assess the respiratory system’s capacity, especially for smokers.
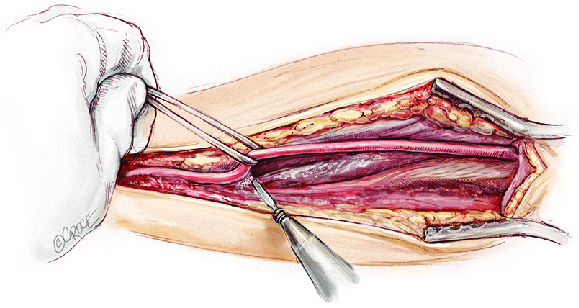
Open Surgical Techniques
Open artery replacement surgery involves complex procedures aimed at bypassing or removing damaged parts of the artery.
These operations require high surgical skill and extreme precision, and are often performed under general anesthesia, with close monitoring of vital body functions.
Liva Hospital in Turkey is renowned for its excellence in performing these complex surgeries, boasting a team of highly experienced surgeons and utilizing the latest surgical techniques.
The specific technique depends on the location and type of the problem:
- Bypass Surgery: This is the most common artery replacement operation. The surgeon creates a new path (bypass) around the blocked or narrowed part of the artery.
A venous graft (a segment of a healthy vein from the patient’s body, usually from the leg) or a synthetic graft (a tube made of a synthetic material such as PTFE or Dacron) is used to connect the healthy artery above the blockage to the healthy artery below it.
For example, in Femoropopliteal Bypass surgery, a blockage in the femoral artery is bypassed using a graft. - Endarterectomy: In this operation, the surgeon makes a small incision in the affected artery and directly removes the accumulated fatty plaque from the inner lining of the artery, restoring normal blood flow.
This operation is commonly performed in the carotid artery (Carotid Endarterectomy) to treat carotid artery narrowings and prevent strokes. - Open Aneurysm Repair: In cases of large or complex aneurysms, the surgeon opens the dilated area of the artery (such as the abdominal or thoracic aorta) and replaces it with a synthetic graft to prevent rupture.
Risks and Complications of Open Surgery
Despite significant advancements in vascular surgery, open artery replacement surgery is considered a major procedure and carries some potential risks and complications, which the patient should be aware of:
- Bleeding: May occur during or after surgery.
- Infection: At the surgical incision site or inside the body.
- Blood Clots: Clots can form in the legs (deep vein thrombosis) or travel to the lungs (pulmonary embolism).
- Heart Attack or Stroke: Due to stress on the heart and blood vessels during surgery, especially in patients with pre-existing heart or vascular conditions.
- Kidney Failure: Kidneys can be temporarily or permanently affected.
- Nerve Damage: May lead to numbness or weakness in the affected area.
- Graft Failure: The implanted graft may not function as expected, necessitating additional intervention.
- Anesthesia Problems: Adverse reactions to medications used in anesthesia.
Recovery Period and Post-Operative Care
Good post-operative care and adherence to lifestyle changes significantly contribute to the long-term success of the operation and prevent recurrence of the problem.
The recovery period after artery replacement surgery begins immediately after surgery and continues for several weeks or even months. It is a crucial stage that requires patience and commitment from the patient.
- Immediately After Surgery: The patient is usually transferred to the Intensive Care Unit (ICU) for close monitoring of vital signs, organ functions, and any signs of bleeding or infection. Pain is effectively controlled.
- Transfer to the Ward: Once stable, the patient is transferred to the hospital ward, where they are encouraged to gradually get up and walk short distances. Instructions are provided on wound care, medication intake, and activities to avoid.
- Vascular Rehabilitation: Vascular rehabilitation is a vital part of long-term recovery.
It includes monitored exercise programs to strengthen limbs and improve blood flow, in addition to education on healthy lifestyle, proper nutrition, smoking cessation, and management of risk factors such as diabetes and high blood pressure. - Regular Follow-up: The patient must adhere to regular follow-up with the surgeon and vascular specialist to assess the condition of the implanted graft, monitor any new symptoms, and adjust the treatment plan when necessary.
Long-Term Outcomes and Improved Quality of Life
Although surgical grafts can last for many years, the patient needs to maintain a healthy lifestyle and manage risk factors to ensure the continued success of the surgery.
Open artery replacement surgery offers excellent long-term results for many patients, leading to a significant improvement in quality of life.
The primary goal of this surgery is to restore adequate blood flow to the limbs and vital organs, thereby:
- Symptom Relief: Patients usually get rid of pain when walking (intermittent claudication) and non-healing skin ulcers.
- Limb Preservation: Surgery significantly reduces the risk of amputation in severe peripheral artery disease cases.
- Prevention of Serious Complications: Carotid artery surgery reduces the risk of strokes, and aneurysm surgery prevents life-threatening rupture.
- Improved Quality of Life: Patients are able to return to their daily activities and live a more active and comfortable life.
Conclusion
In conclusion, open artery replacement surgery is a complex and life-saving surgical procedure that offers an effective solution for serious arterial diseases.
Thanks to advanced surgical expertise, sophisticated techniques, and comprehensive pre- and post-operative care, patients regain the ability to live a normal life without the limitations of pain and complications.
It is a testament to modern medicine’s immense ability to rebuild the “arteries of life” in our bodies, offering hope for a healthy and vibrant future for everyone who needs this specialized care.
Liva Hospital in Turkey provides an ideal environment for this surgery, with all the necessary modern technology and excellent care.
To achieve the best results, patient adherence to the rehabilitation plan and lifelong regular follow-up is essential.
Frequently Asked Questions
How long does open artery replacement surgery take?
The duration varies depending on the affected artery and the complexity of the case, but it usually ranges from 3 to 6 hours, or more in some complex cases.
Is open surgery the only option for artery replacement?
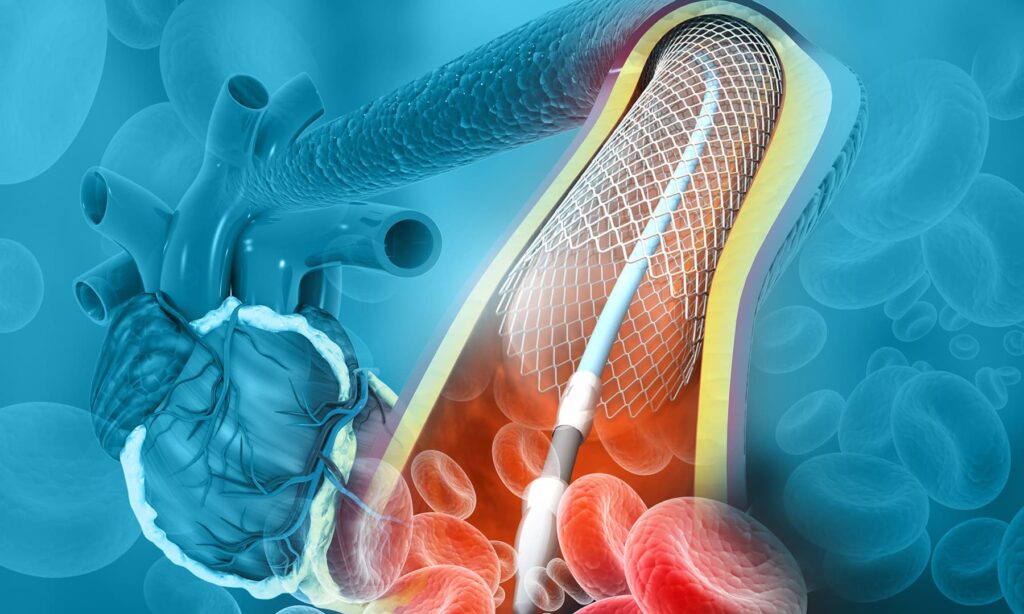
No, not always. There are alternatives such as catheterization and stent placement or endovascular procedures, which are less invasive.
How long is the recovery period after artery replacement surgery?
Full recovery typically ranges between 6 to 12 weeks, but symptom improvement may be noticed within a few weeks after surgery.
Can artery blockage problems recur after surgery?
Yes, despite successful surgery, new blockages can develop in other arteries or even in the implanted graft if underlying risk factors (such as smoking, diabetes, high cholesterol, and high blood pressure) are not effectively controlled.
What restrictions will I face after surgery?
Initially, there may be restrictions on heavy lifting or driving, and you may be asked to avoid some strenuous physical activities. Your doctor will provide you with detailed instructions on safe and prohibited activities during the recovery period.
Is age a decisive factor in determining the possibility of surgery?
Age alone is usually not the decisive factor. More important is the patient’s general health, the presence of other chronic diseases, and the body’s ability to tolerate and recover from surgery. Each case is evaluated individually.