Unfortunately, cardiovascular diseases remain the leading cause of death worldwide, with coronary artery stenosis, also known as coronary artery disease, being prominent among them.
Arterial narrowing results from the buildup of fatty plaques within the walls of the arteries that supply the heart muscle, reducing blood and oxygen flow to the heart.
For decades, treatment options were limited, but thanks to tremendous advancements in medical technology and intensive research, we have witnessed a true revolution in the methods of diagnosing and treating this condition.
It is no longer limited to traditional solutions; today, a wide range of innovative techniques offer new hope to patients and significantly improve their quality of life.
Coronary Artery Stenosis
Coronary artery stenosis is a condition that develops slowly over many years, often without clear symptoms in its early stages.
Fatty plaques are composed of cholesterol, other fatty substances, calcium, and other materials in the blood, accumulating on the inner walls of the arteries.
Over time, these plaques harden and narrow the arteries, reducing their flexibility and impeding the flow of oxygen-rich blood to the heart muscle.
This lack of blood supply can lead to angina (chest pain), shortness of breath, and in severe cases, can result in a heart attack or heart failure.
Early and effective therapeutic intervention not only alleviates symptoms but also prevents serious complications and increases survival rates.
Understanding the pathophysiology of arterial narrowing is the first step towards choosing the optimal treatment tailored to each patient’s condition.
Cardiac Catheterization and Drug-Eluting Stents
Cardiac catheterization with stent placement remains a cornerstone in the treatment of coronary artery stenosis, but it has undergone tremendous developments over the years.
Bare metal stents were the first option, but science evolved to Drug-Eluting Stents (DES), which release medications to prevent re-narrowing of the artery.
These drug-eluting stents, specifically designed to reduce the chance of restenosis, represent a qualitative leap in patient outcomes.
New generations of these stents have also emerged, characterized by more flexible designs and adaptability to arterial anatomy, in addition to biocompatible materials that reduce inflammatory response.
These techniques are the most common and effective option in many cases of arterial narrowing, and specialized hospitals like Liva Hospital in Turkey offer them with the highest international quality standards, providing patients with safe and effective solutions.
Complex Revascularization Techniques
For more complex cases, where the narrowing is severe or located in difficult-to-reach arteries, advanced revascularization techniques have emerged.
Prominent among these is the use of CT-PCI Overlay, which allows doctors to visualize arteries in 3D and determine the optimal catheter path.
We have also seen developments in Drug-Coated Balloons (DCB), which deliver medication directly to the arterial wall without leaving a permanent stent, reducing the risk of late thrombosis and providing greater arterial flexibility.
For severe calcifications, techniques such as Intravascular Ultrasound (IVUS) and Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) are used to precisely assess the artery from within, helping to choose the most appropriate tool for breaking down calcifications, such as Rotational Atherectomy.
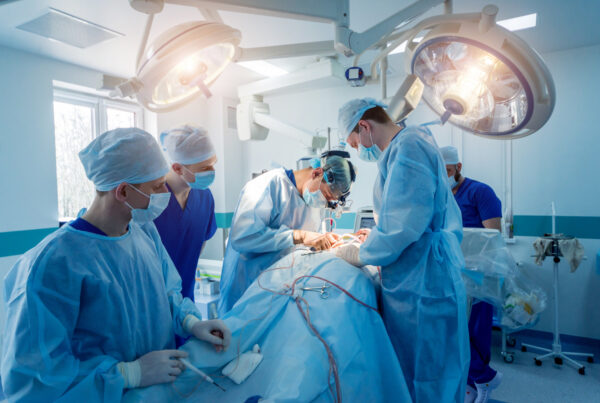
Advanced Surgical Treatment
Despite advances in catheter-based interventions, Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG) remains a vital option, especially for patients with multiple severe narrowings, or in certain cases where catheterization is not suitable.
This surgery has also undergone significant developments. There is an increasing trend towards Minimally Invasive CABG, where surgery is performed through small incisions instead of the traditional large sternal incision.
The focus is also on Off-Pump CABG, performed without the use of a heart-lung machine, which reduces complications associated with machine use.
Additionally, 3D imaging techniques and surgical robots are used to increase surgical precision and reduce patient recovery time. These developments have made open-heart surgery safer and more effective for patients who need it.
Promising Future Treatments
Scientific research continues to unveil new horizons in the treatment of coronary artery stenosis, and there are many promising treatments that herald a better future.
Stem Cell Therapy aims to repair damaged tissues in the heart and arteries, and some initial studies have shown encouraging results in improving heart function.
Gene Therapy seeks to introduce specific genes into cells to improve the growth of new blood vessels or modify the response to inflammation and plaque accumulation.
Research is also ongoing into 3D Printing techniques to create accurate models of the heart and arteries, helping surgeons plan complex operations with greater precision, and even print replacement biological tissues in the future.
Recent reports indicate the integration of Artificial Intelligence in diagnosis and treatment planning, such as the CathAI algorithm for analyzing coronary images with over 90% accuracy in detecting stenosis.
Personalized treatment approaches are also being explored, where metabolomics and genomics help predict response to treatment and tailor the procedure according to arterial structure and stenosis severity.
These techniques, although still in early research stages, hold immense potential to radically change the course of heart disease treatment.
Conclusion
We have witnessed qualitative leaps in the treatment of coronary artery stenosis, transforming the perception of this disease from a death sentence to a condition that can be effectively managed.
From advancements in catheterization and drug-eluting stents to advanced surgical techniques and promising treatments such as stem cell therapy and gene therapy, scientific and medical efforts are combined to provide the best possible care for patients.
Continuous research and innovation are what drive progress in this vital field. Thanks to leading medical institutions like Liva Hospital in Turkey, which adopts the latest technologies and invests in medical competencies, patients today can look forward to a brighter future, enjoying healthy hearts and a better life.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between catheterization, balloon angioplasty, and stenting?
Catheterization is the general procedure where a thin tube (catheter) is inserted into the arteries. Balloon angioplasty is part of catheterization, where a small balloon is inflated inside the narrowed artery to widen it.
Are drug-eluting stents better than bare-metal stents?
Generally, yes. Drug-eluting stents release medications that prevent cell growth within the artery, significantly reducing the risk of restenosis compared to bare-metal stents.
When do doctors prefer coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) over catheterization?
Bypass surgery is usually preferred in cases of multiple and severe arterial narrowings, or when the narrowings are in difficult-to-reach areas with catheterization, or in some cases where the patient has diabetes or heart failure.
Can coronary artery stenosis be prevented?
Yes, coronary artery stenosis can be largely prevented by adopting a healthy lifestyle that includes a balanced diet, regular exercise, controlling risk factors such as high blood pressure, diabetes, and cholesterol, and quitting smoking.
Is stem cell therapy currently available for treating arterial stenosis?
Stem cell therapy is still in the research and clinical trial phases and has not been widely adopted as a routine treatment for coronary artery stenosis. There are promising results, but more studies are needed to determine its long-term effectiveness and safety.
What is the importance of regular heart check-ups?
Regular heart check-ups are essential for early detection of any signs of arterial narrowing or other heart diseases, even before obvious symptoms appear. This allows for early therapeutic intervention, increasing the chances of success and preventing serious complications.